In this article on “Introduction to the Piano,” we’re going to dive into the basics of the piano. And here’s the list of topics we’ll be covering:
Introduction to the Piano
- Brief history and significance of the piano in music culture
- Explanation of why it’s a popular instrument for beginners and professionals alike
Piano Keys Layout
- Detailed explanation of the layout of the piano keys, distinguishing between the white and black keys
- Introduction to the concept of octaves and how they are represented on the keyboard
Finding Middle C
- Step-by-step guide to locating the middle C key on the piano
- Importance of middle C as a reference point for learning and understanding piano music
Introduction to the Piano
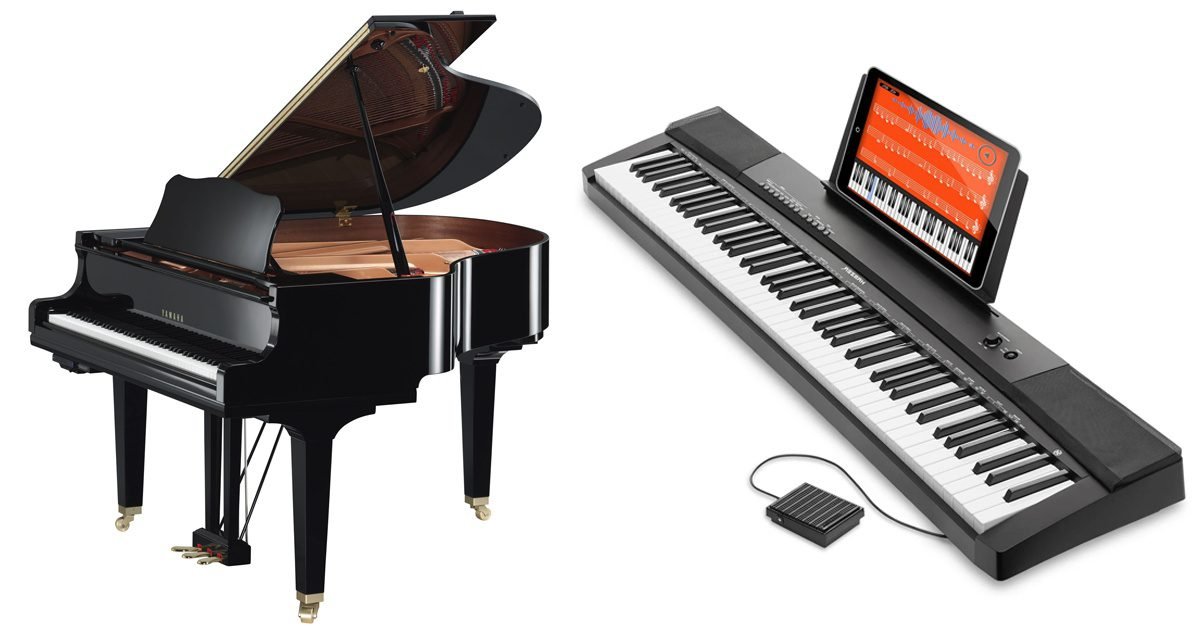

The Piano – A Classic Instrument
The piano, invented by Bartolomeo Cristofori of Italy in the early 1700s, quickly became a favorite among musicians for its expressive range and dynamic capabilities.
Originated in the early 1700s, it has evolved significantly earlier keyboard instruments like the harpsichord and clavichord to the grand acoustic piano and electronic musical keyboards.
Its ability to produce both soft and loud sounds (hence its name, “pianoforte”) revolutionized music composition and performance.
The Electronic Musical Keyboard
In comparison, the electronic musical keyboard is a relatively new invention.
The first electronic keyboards emerged in the mid-20th century, with significant advancements in the 1980s.
These instruments use digital technology to replicate the sounds of traditional pianos and other instruments. Because of this digital technology, it can create a wide range of tones and effects.
Why Piano is So Popular
Unlike many instruments, the piano can produce both soft, delicate sounds and powerful, resonant chords, making it incredibly versatile.
The piano’s accessibility is one reason it is so popular.
For beginners, it offers a clear visual representation of musical notes, making it easier to learn the basics of music theory and practice.
For professionals, the piano provides a platform to explore complex compositions and innovate within their craft. Its ability to cater to both novice and expert musicians alike is a testament to its enduring appeal.
Anatomy of the Piano
Before we jump into the layout of the keys, let’s take a moment to understand the structure of the piano.
At first glance, the piano might seem like a simple instrument, but it comprises several intricate components that work together to produce its beautiful sound.
The Keyboard
The most recognizable part of the piano is its keyboard, typically composed of 88 keys.
These keys are divided into white and black keys, each serving a specific purpose in creating music.
The keyboard is where your fingers dance to bring melodies to life.
The Pedals
Pianos also feature pedals at the base, usually three in number.

The damper pedal (right) sustains notes;
the soft pedal (left) reduces volume and alters tone; and
the sostenuto pedal (middle) sustains selected notes.
These pedals enhance the instrument’s versatility and expressiveness.
Internal Components
Inside the piano, a complex mechanism involving hammers and strings converts the pressing of keys into musical notes.
A hammer strikes a string when you press a key, creating a sound.
The length, thickness, and tension of the string determine the pitch of the note.
This ingenious design allows the piano to offer such a wide range of notes.
Piano Keys Layout
Understanding the layout of the piano keys is a fundamental step for any aspiring pianist.
This knowledge will help you read music, find notes quickly, and play more confidently.
We’ll briefly touch on this topic here. However, part three of the series will cover it in detail, including a thorough breakdown of each note (C, D, E, F, G, A, B), how notes are placed on the keyboard and sheet music, and the concepts of whole steps and half steps.
White Keys
The white keys on the piano represent the seven natural notes of the musical alphabet: A, B, C, D, E, F, and G.

These keys repeat in the same order across the entire length of the keyboard. Each white key corresponds to a specific note, making it straightforward to locate and identify them.
Black Keys
The black keys are arranged in groups of two and three and correspond to the sharps and flats in music.
They are positioned slightly above and between the white keys. The pattern of black keys helps to quickly identify the positions of the white keys and navigate the keyboard efficiently.
Octaves
An octave consists of eight notes and spans from one note to the next occurrence of the same note.
For instance, the keyboard transitions from one C to the subsequent C.
The piano’s 88 keys cover a little more than seven octaves, providing a vast range of notes to play.
Understanding octaves is crucial for both playing and composing music, as it helps you recognize patterns and structures in musical pieces.
Finding Middle C
One of the first milestones for any piano student is finding the middle C.
This note serves as a central reference point for learning and understanding piano music.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Locate the Center of the Keyboard:
Stand in front of the piano and look for the keyboard’s center. This is usually around the logo of the piano brand.
- Identify the Black Keys:
Look for the black keys arranged in groups of twos and threes. These groups repeat across the keyboard.
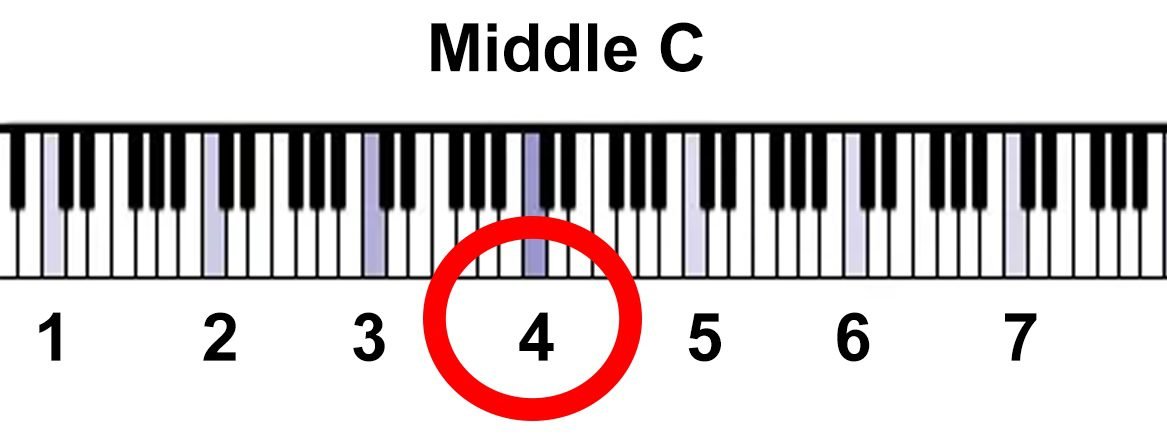
- Find the Closest Group of Two Black Keys:
In the middle of the keyboard, locate the group of two black keys closest to the center.
- Spot the White Key to the Left:
As shown in the image, the white key immediately to the left of these two black keys is the middle C.
Importance of Middle C
Middle C is often the starting point for beginners because it divides the keyboard into two equal parts.
It also corresponds to the note that sits on the ledger line between the bass and treble clefs in sheet music, making it a crucial reference point for reading music.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we talked about the piano, its history, how it works, and where the keys are.
We also talked about the white and black keys, what octaves are, and how to find the important middle C. These are important things to know if you want to start playing the piano or just enjoy it more.
We hope this guide helped you learn something new and got you excited about playing the piano. Remember, there’s a lot to discover in music, so keep exploring and have fun playing!